Your GO-TO team for complex regulatory and code compliance
Spaces are created to seamlessly adjust to many scales of operation without compromising efficiency or patient care.
The Risk Assessment will evaluate systems or equipment and assign one of the four risk categories:
- Category 1: Failure is likely to result in major injury or death
- Category 2: Failure is likely to cause minor injury
- Category 3: Failure is not likely to cause injury but can cause discomfort
- Category 4: Failure has no impact on patient care
The category meanings of Chapter 4 are then applied to the requirements in Chapters 5-11.
Source: The above information is from a presentation from the Pennsylvania Department of Health at the 2023 Spring Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
- CMS S&C Letter 17-15-LSC
- Updates FSES requirements from 2001 NFPA 101A to 2013 NFPA 101A to reflect adoption of the 2012 LSC
- FSES can be completed by the facility, a trained consultant or the SA at their discretion
- FSES is submitted to the SA for review
- New requirements:
- The DA must send the FSES to the CMS RO for final approval as part of the Plan of Correction
- FSES must be completely new at each annual (or other survey frequency depending on facility type) survey and must reflect the results of the SA LSC survey

Source: The above information is from a presentation from the Pennsylvania Department of Health at the 2023 Spring Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
If the project intends to follow the FGI Guidelines, an SRA must be conducted to deliver safe care. The SRA was added to the FGI Guidelines in the 2014 edition and is made up of seven key areas included below.
- Infection Control Risk Assessment
- Patient Handling and Movement Assessment
- Patient Fall Prevention
- Medical Safety
- Behavioral and Mental Health (Psychiatric Patient Injury and Suicide Prevention)
- Patient Immobility
- Security Risks
The only way one of these key areas can be skipped is when it is not applicable to the project.
Not more than 10 gallons of ABHR solution or 1,135oz of Level 1 aerosols, or a combination of solution and aerosols, shall be used outside of a storage cabinet in a single smoke compartment, with the exception of the following:
- One dispenser per room and located in that room shall not be included in the aggregate total.

Source: The above information is from a presentation from the Department of Health at the 2023 Spring Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
In the last several days, the United States government and the World Health Organization (WHO) have lifted emergency status declarations for the COVID 19 pandemic. Three years after this unwelcome illness first surfaced, we can safely stop calling this a pandemic.
But JPT knows this doesn't mean we're done because COVID-19 is here to stay. New variants will consistently emerge and we need to still be vigilant in protecting ourselves. COVID-19 is still causing infections. COVID-19 is still killing people. It's just doing it at low numbers compared to what it was doing three years ago.

The love of life or living things is the definition of Biophilia. Human beings enjoy nature and it is imperative to our health and well-being.
Biophilic design goes along with principles of biophilia to integrate elements of nature into built environments in Architecture and Interior Design.
Many healthcare organizations have gotten away from the “clinical” look to utilize design strategies that make patients, staff and other guests feel good. Biophilic Design is a great way to do this.

There is an exception if the door leaf is equipped with an approved self-closing device and is not required by code to swing in the direction of egress travel.
The Life Safety Code is not intended to apply to the swing of cross-corridor doors, such as horizontal exits and smoke barrier doors.
Both of these requirements are not meant to apply to doors from rooms that are mostly unoccupied, such as closets used by maintenance, electrical or telecommunications.

Source: The above information is from a presentation on the Life Safety Code at the 2022 Fall Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
In addition to the need for a risk assessment, water management plan, and testing protocols and acceptable ranges, this standard also includes more water management program specifics such as an individual or team being responsible for the oversight and implementation of the water management program. This oversight and implementation of that program includes development, management and maintenance activities. Other required elements of the water management program are a basic diagram that maps water supply sources, treatment systems, processing steps, control measures and end-use points.
This standard was evaluated by the Joint Commission and last updated on January 1, 2022.

What are Tele-ED's eligibility criteria?
- A hospital in a rural area with 46.0 or less average daily emergency department visits over a two-year period is considered an "eligible rural hospital".
- Any area not included in an "urbanized area" by the US Census Bureau based on the 2010 decennial census is considered a "rural area".
- Eligibility is determined using the US Census Bureau's mapping tool. Eligible locations for Tele-ED are all the areas that are not in an urbanized area (blue areas).

Source: The above information was included in a presentation by the Division of Acute and Ambulatory Care (DAAC) from the PA Department of Health at the 2022 Fall Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
These factors include:
- Full compliance of provisions that apply to new atriums, the boundary is constructed as a smoke partition and doors must have a positive latch.
- Must be permitted by occupancy chapter.

Source: The above information is from a presentation on the Life Safety Code at the 2022 Spring Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
The main licensed hospital must be fully integrated with the OED. Additionally, the main licensed hospital must be located within a 35-mile radius of the OED.

Source: The above information is from a presentation by the Pennsylvania Department of Health at the 2022 Fall Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
During a fire training drill, the time required to evacuate all persons from a hyperbaric area with a full complement of chamber occupants all at treatment pressure shall be measured on a yearly basis. The occupants may be simulated for this training drill.

Source: The above information is from a presentation by The Joint Commission at the 2022 Fall Pennsylvania Society of Healthcare Facility Engineers (PSHFE) conference in Harrisburg, PA.
To its adjacent spaces, operating rooms are to be in a positive air pressure relationship. This is based on the code-required ventilation standards.
Although there are no provisions for COVID-19, there are organizations that have created negative pressure anti-rooms for their ORs.
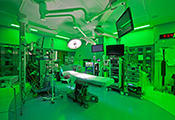
Source: The above information is from a presentation by The Joint Commission at the 2022 annual American Society of Healthcare Engineers (ASHE) conference in Boston, MA.
Looking at recent national public health issues such as SARS, Ebola and H1N1 we have greater insight on how important appropriate ventilation is in limiting the spread of pathogens. While it can be surmised that an overall increase in airborne infection isolation rooms, and negative pressure patient treatment spaces should be considered, the Joint Commission cannot make a prescriptive recommendation on this space planning issue.

Source: The above information is from a presentation by The Joint Commission at the 2022 annual American Society of Healthcare Engineers (ASHE) conference in Boston, MA.
All facilities are expected to make changes to their emergency plan in the event changes are required more frequently outside of their update cycles.
The exception to this is for Long Term Care Providers who should review their emergency plan every year.

Source: The above information is from a presentation by DOH regarding CMS Survey Guidance.
- Meet ICU criteria
- Available OR with temp of 95 degrees
- Maximum of one patient per room
- Patient room designed with Protective Environment (PE)
- Radiant heat panels over bed
- Direct access to a patient toilet room

Source: The above information is from a presentation by FGI at the ASHE Annual Conference in 2021
The following list completes the order of priority in which DAAC executes surveys since April of 2021:
- Federal EMTALA Surveys
- Federal Compliant Surveys
- Federal Recertification, Validation Surveys, and Transplant Surveys
- State Licensure Renewal Surveys
- State Complaint Surveys
- Occupancy Survey in Hospitals and Ambulatory Surgical Facilities (ASFs)
- New State Licensure
- Occupancy Survey for Hospital Outpatient Facilities
- New CMS Certification
Source: The above information is from a presentation by DAAC at the Healthcare Facilities Management Association of Delaware Valley during the Spring 2021 conference.
The following list completes the order of priority in which DAAC executes surveys since April of 2021:
- Federal EMTALA Surveys
- Federal Compliant Surveys
- Federal Recertification, Validation Surveys, and Transplant Surveys
- State Licensure Renewal Surveys
- State Complaint Surveys
- Occupancy Survey in Hospitals and Ambulatory Surgical Facilities (ASFs)
- New State Licensure
- Occupancy Survey for Hospital Outpatient Facilities
- New CMS Certification

Source: The above information is from a presentation by DAAC at the Healthcare Facilities Management Association of Delaware Valley during the Spring 2021 conference.
Medical Behavioral and Mental Health sections of the hospital are recommend to have a ceiling height of 9' as this reduces the potential for self-harm.

Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines in 2022.
Medical Behavioral and Mental Health sections of the hospital are recommend to have a ceiling height of 9' as this reduces the potential for self-harm.

Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines in 2022.
Below are changes made in the hospital Guidelines within the NICU:
- The minimum clear floor area of multiple-infant rooms has been increased from 120 to 150 square feet.
- The minimum clear floor area of single-infant rooms has been increased from 165 to 180 square feet.

Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines in 2022.
The use of the chapter on Critical Access or Small Hospitals may be implemented within a hospital with 35 or less licensed beds.

Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines in 2022.
A modular or prefabricated laminar flow ceiling system is needed if:
- Seams/access doors gasketed
- Structurally rated assembly
- Access for testing, maintenance and replacement
- Diffuser complaint with ASHRAE 170
Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines for 2022.
Whether an Anteroom is required shall be decided by an Infection Control Risk Assessment (ICRA). Deciding factors include defining the intended use, facility location and long-range infection avoidance planning.
Source: The above information is an update to FGI Guidelines in 2022.
The minimum door opening length for Elevators has been reduced from 54" to 48".

Source: The above information is an update to hospital FGI Guidelines in 2022.
Non-recirculated fixture branch piping has been changed from having a maximum of 25 feet to a maximum of 10 feet.

Source: The above information is an update to hospital FGI Guidelines.
Non-recirculated fixture branch piping has been changed from having a maximum of 25 feet to a maximum of 10 feet.

Source: The above information is an update to hospital FGI Guidelines.
Sometimes, wayfinding and signage don’t cut it when someone is in distress and looking to receive help from the hospital. These new implementations are a direct result of Laura’s Law which was put into place because a husband believes that his wife’s death could’ve been avoided if she had the ability to find an unlocked door to the emergency room. The husband accredits poor signage and a lack of video surveillance monitored by the hospital as the reasons why his wife succumbed to an asthma attack only feet away from the hospital’s front door.

Source: The above information is an update to hospital FGI Guidelines.
A plan of action should include a system to study the facility's needs based on the defining characteristics of an EID that includes:
- Increased need for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Options for screening staff, patients and other hospital guests; which may also include testing options for infectious diseases
- Transfers or discharges of patients
- Settings in home-based Healthcare
- Changes in physical environment such as distancing, isolation and capacity/surge
Source: All information was found from the Pennsylvania Department of Health
Following the NFPA's Life Safety Code (NFPA 101-2012), Section 7.3.4.1(2), this requirement was based on the root chapter on egress. This chapter sets the minimum width of any means of egress at 36 inches in all facilities or sections of facilities classified as healthcare occupancy.

Source: All information was found on The Joint Commission
Changes in response to the current COVID-19 pandemic have to be included in the facility's Emergency Preparedness Plan and documented.
- The only time these changes apply is during the emergency.
A collaborative approach can bring about effective and affordable solutions to contain these high patient volumes. Below are some considerations:
- Ask the right questions EARLY on in the process
- Mix in multi-patient and flexible treatment spaces (Multi-patient rooms allow a family to be treated together)
- Create a privacy room option by creating a space to merge another bed in the patient rooms so they can be single or multiple-use depending on the circumstance
- Reconfigure and enlarge ED space when possible

Design Considerations for Sound Management
- Consider traffic and noise levels with the function of the space
- Add drop down door seals (Easy and cost effective)
- Add acoustic absorbers
- Don't position the doors directly across from one another
- Insulate walls where possible
- Lining in ducts

Onstage refers to spaces used only by the public or patients, their families, and guests. Offstage refers to behind-the-scenes spaces used only by staff or healthcare staff members and patients/guests escorted by staff. Disney’s Onstage/Offstage environmental model can provide the following advantages:
- Better healing environment
- Increased infection control
- Less crowded spaces
- More open layout
- Quicker in-room deliveries
- Reduction in unpleasant aromas
- Elevated security
- Heightened collaboration
- Quieter setting

- Magnify the use of technology to personalize care
- Offer control and customization over their work environment
- Minimize the risk of exposure to germs and pathogens

To establish a safe and comfortable setting in the outpatient environment, specific strategies need to be implemented.
- Decrease patient contact with "shared" surfaces as much as possible
- Removing items from common spaces (magazines, books and toys)
- Eliminate all sources of shared water drinking (water fountains and dispensers)
- Seating spaces 6 feet apart at least
- Develop alternate seating arrangements if possible
As Healthcare Designers, we need to put staff spaces as a fore-thought instead of an after-thought. Usually, hospitals have the essentials, such as lockers, restrooms and staff lounges, but some of the elements mentioned below need implemented at some level.
- Outdoor Space/Incorporations of Nature
- Privacy
- Mixed high-top seating and lounge furniture
- Quite

Even though clinicians and staff members do interact with patients, offering off-stage staff circulation and dissemination could decrease exposure to the COVID-19 virus. Corridors could be made wider so that a two-way flow could occur with the correct amount of distance.

Some hospitals have even taken to using tents outside of their ED and with the rising number of individuals becoming infected with COVID-19, triaging patients before they enter the ED could help make the intake process smoother. Triaging patients during intake would mean to prioritize their level of care based on illness/injury, severity, prognosis and resource availability. Specifically, in today’s modern society, we should have ways to triage patients before they even walk in the front door by offering telemedicine options, apps, multiple entries and other waiting solutions based upon medical needs.

One of the best ways to ensure more bed capacity and safety to patients is by using available shell space for temporary bed space. Even if there is an opportunity to create shell space for temporary bed space with an accelerate design and construction schedule, that is a valid option as well. The created space can then be used for any hospital department after it's no longer needed for COVID-19 patients.
JPT found this out because we saw a pattern of our clients coming to us for help creating fast-track, build-out of shell spaces to accommodate beds and nursing support spaces.
Virtual solutions offered by The Joint Commission can be found below.
- Durable Medical Equipment Point of Service (DMEPOS) providers can now obtain Medicare recognition by a virtual survey option for both initial and resurveys
- Initial licensure survey (home health/hospice in California and Florida)
- Initial Medicare certification survey (home health/hospice)
- Hospice organizations within the state of California who have received a temporary license

All information was found on The Joint Commission's website.
High-quality viral filters can be inserted between the breathing circuit and the patient's airway and between the expiratory limb and the machine. In order to prevent contamination of the machine, JPT sees these filters as essential.
Note: Breathing circuits should be thrown away after every use even with these high-quality filters.
The new and revised COVID-19 blanket waivers below were either added and/or modified.
- Alcohol-Based Hand Rub (ABHR) Dispensers: "CMS is waiving the prescriptive requirements for the placement of alcohol-based hand rub (ABHR) dispensers for use by staff and others due to the need for the increased use of ABHR in infection control. However, ABHRs contain ethyl alcohol, which is considered a flammable liquid, and there are restrictions on the storage and location of the containers. This includes restricting access by certain patient/resident population to prevent accidental ingestion. Due to the increased fire risk for bulk containers (over five gallons) those will still need to be stored in a protected hazardous materials area. Refer to: 2012 LSC, sections 18/19.3.2.6. In addition, facilities should continue to protect ABHR dispensers against inappropriate use as required by 42 CFR @482.41(b)(7) for hospitals; @485.623(c)(5) for CAHs; @418.110(d)(4) for inpatient hospice; @483.470(j)(5)(ii) for ICF/IIDs and @483.90(a)(4) for SNF/NFs."
- Fire Drills: "Due to the inadvisability of quarterly fire drills that move and mass staff together, CMS will instead permit a documented orientation training program related to the current fire plan, which considers current facility conditions. The training will instruct employees, including existing, new or temporary employees, on their current duties, life safety procedures and the fire protection devices in their assigned area. Refer to: 2012 LSC, sections 18/19.7.1.6."
- Temporary Construction: "CMS is waiving requirements that would otherwise not permit temporary walls and barriers between patients. Refer to: 2012 LSC, sections 18/19.3.3.2."

Updated guidance to recommend that nursing homes:
- Act now to implement all COVID-19 preparedness recommendations, even before cases are identified in their community
- Address asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission, implement source control for everyone entering a healthcare facility (e.g., healthcare personnel, patients, visitors), regardless of symptoms.
- Cloth face coverings are not considered personal protective equipment (ppe) because their capability to protect healthcare personnel (HCP) is unknown. Facemasks, if available, should be reserved for HCP.
- For visitors and residents, a cloth face covering may be appropriate. If a visitor or resident arrives to the facility without a cloth face covering, a facemask may be used for source control if supplies are available.
- Dedicate an area of the facility to care for residents with suspected or confirmed COVID-19; consider creating a staffing plan for that specific location

These actions can preserve staff personal protective equipment (PPE) and patient care supplies; ensure staff and patient safety; and expand available hospital capacity.
- Delay all elective ambulatory provider visits
- Reschedule elective and non-urgent admissions
- Delay inpatient and outpatient elective surgical and procedural cases
- Postpone routine dental and eyecare visits

Healthcare designers need to create value by designing hospitals that allow patients along with their families' to have a more enjoyable experience with long-term stays.
Solutions:
- All-in-one operating rooms and patient rooms.
- Influences from the hospitality and retail markets help to create a warm and non-clinic feel.
- Personalized service and attention to detail can make all the difference in the patient’s experience.
- Healthcare systems use data from previous patients to offer more personalized solutions for current and future patients.

- Screen patient and visitors for stmptoms of acute respiratory illness (e.g. fever, cough, difficult breathing) before entering your healthcare facility. Keep up to date on the recommendations for preventing the spread of COVID-19.
- Ensure propser use of personal protection equipment (PPE). Healthcare personnel who come in close contact with confirmed or possible patients with COVID-19 should wear the appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Conduct an inventory of available PPE. Consider conducting an inventory of available PPE supplied. Explore strategies to optimize PPE supplies.
- Encourage sick employees to stay home. Personnel who develop respiratory symptoms (e.g., cough, shortness of breath) should be instructed not to report to work. Ensure that your sick leave policies are flexible and consistent with public health guidance and that employees are aware of these policies.

- Stay informed about the local COVID – 19 situation. Know where to turn for reliable, up-to-date information in your community. Monitor the CDC COVID – 19 website and your state and local health department websites for the latest information.
- Develop, or review your facility’s emergency plan. A COVID – 19 outbreak in your communication could lead to staff absenteeism. Prepare alternative staffing plans to ensure as many of your facility’s staff are available as possible.
- Establish relationships with key healthcare and public health partners in your community. Make sure you know about healthcare and public health emergency planning and responsive activities in your community. Learn about plans to manage patients, accept transfers, and share supplies. Review any memoranda of understanding (MOUs) with affiliates, your healthcare coalitions, and other partners to provide support or assistance during emergencies.
- Create an emergency contact list. Develop and continuously update emergency contact lists for key partners and ensure the lists are accessible in key locations in your facility. For example, know how to reach your local or state health department in an emergency.

- Suicide Prevention
- High-Level Disinfection/Sterilization
- Sterile Compounding
- Hemodialysis

The combination of HEPA filtration, high numbers of air changes per hour (>12 ACH), and minimal leakage of air into the room creates an environment that can safely accommodate patients who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
- Guidance when exam/treatment, procedure and operating rooms are needed
- Clearance and spatial relationships
- Locations for procedure types
- Design of telemedicine spaces
- Sterile processing facilities
- Mobile/transportable medical unit

The six (6) key topics of the Acoustical Design "Tool-Box" according to the FGI Guidelines are:
- Site Exterior Noise
- Acoustical Finishes and Details
- Room Noise Levels
- Sounds Isolation & Speech Privacy
- Electro - Acoustics - Alarms, Sound Masking
- Vibration

The differentiating factor would be that protective environment rooms require positive air pressure relative to adjoining spaces with all supply air passing through HEPA filters. Basically, these rooms help to protect patients with compromised immune systems.
Surface markings may be paint, reflective paint, reflective markers or preformed material. Additionally, lines/markings may be outlined with a 6-inch wide (15 cm) line of a contrasting color to enhance conspicuity.

- Planning
- Schematic Design
- Design and Development
- Construction Documents
- Construction
- Commissioning

Below are some of the common design challenges that are unique to critical access hospitals:
- Construction costs can be increased based on scarce resources
- Difficulty finding specialists to provide care
- Lack of patient transportation
- Lack of technology
- Patient population income level distinctions and inability to afford healthcare
- Recruitment efforts are weak due to small labor pool
- Remote location makes getting access to care difficult

An exception is given for renovation of existing space, provided there is a minimum floor area of 150 ft2.
It is up to the facility to make sure that contracted individuals receive the proper training on the facility's emergency plan, important contract information and the facility's expectations for those individuals during an emergency. Additionally, if a surveyor asks one of these Contracted Individuals what their role is during a disaster, or any relevant questions, then the expectation is that the Contracted Individual can describe the emergency plans/their role.
- A new table has been added to help designers and facility owners determine which procedures should be performed in each room type.
- Note: Do not add procedures or services in any existing rooms based on the chart without first checking with DAAC
Source: All information obtained from DOH speaker at the Healthcare Facility Managers Association of Delaware Valley 2019 Spring Conference
It is a good idea to designate a room with chairs for this 15-minute part of the survey as everyone can have an open discussion. The purpose of the Opening Conference is for introductions and to go over every element of the survey agenda.

Airborne infection isolation room doors and doors to the anteroom, if provided, are now permitted to be self-closing or equipped with an audible alarm.

Source: This information was obtained from the Healthcare Facility Managers Association of Delaware Valley in the Spring of 2019.
- Acknowledge and welcome surveyor(s)
- Look at surveyor’s Joint Commission issued ID to ensure identification
- Have a location ready for surveyor(s) to wait while step 4 is executed
- Confirm the validity of survey by having a pre-designated staff member access system’s Joint Commission extranet site
Note that staff members should be aware of these steps and know who is responsible for each one. Having a backup plan is also important in case staff members are on vacation or sick.

If your hospital has or is getting equipment to facilitate the use of Nitrous Oxide as a pain reliever for women giving birth, you must do more than just notify Department of Health (DOH). Currently, DOH is in the process of coming up with standards for Nitrous Oxide equipment. Also, read the manufacturer’s instructions associated with the equipment.

When redesigning aged healthcare facilities, it is important to keep the following tips in mind.
- Find the existing drawings
- Go in with your design team for a very hands-on survey
- Incorporate some restoration of the building if possible
- Have a discussion on phasing conditions

The best ways to reduce water usage are within patient rooms, general bathrooms and employee pantry sinks by specifying low-flow and flush water fixtures where possible. Utilizing non-potable water for mechanical equipment is another way to reduce usage. The energy efficiency of your hospital also plays hand in hand with water consumption.
Clinical-use water fixtures such as surgical scrub and exam sinks are necessary in order to prevent the spread of infection. These types of fixtures are even excluded from LEED due to their value in human health.

The large size of this equipment requires thought in deciding how it will be directed through or around the facility to its desired location. Does it need to be lifted or can a route be deciphered through the hospital? Make sure to discuss this with equipment vendors and have your design team help to make this decision.
The following are tips for designing an efficient operating room:
- User Group Info – get this early
- Plan for Realistic Volume
- Right-Size Room – according to type of surgical procedure
- Infection Prevention
- Technology – have the best and most advanced
- Proper Ventilation
- A Micro-Hospital is a small-scale, inpatient facility with 8-15 short-stay beds.
- The number one benefit in creating one of these facilities is to cut costs.
- Currently, there are about 60 Micro-Hospitals in the US and they are mainly providing patient care in under-served urban locations.
- Note: If you are thinking about creating a Micro-Hospital, any kind of market analysis needs to be followed through with. Due to the small size of these Micro-Hospitals, adding and upgrading within these locations can quickly coincide what you set out to do in the first place. What is meant by this is that the square-footage and bed count can increase quickly, eliminating the cost benefits of a “micro” facility.
Below are some unique tips to consider when designing waiting rooms in a healthcare environment.
- Introduce your facility by providing information on doctors, infrastructure upgrades and innovative or new care that is being provided.
- Seating arrangements should be clustered, so both single patients and patients who brought guests along are accommodated.
- Provide text updates to patients while they are in the waiting room.
- Space should be open but with two sections - one section with a TV and another that is quiet for relaxation.
- Chairs should have high armrests. This helps patients get in and out of chairs easily.
- Natural light should be included as much as possible.

- Sinks for hand washing only (non-patient use)
- Movement sensor start and stop sinks
- Hand drying options should include paper towels only – no hand dryer machines
- Wall hand sanitizer dispensers near all hospital entrances, patient rooms (private and semi-private), nurse stations, hallways and food service areas
- To make hand sanitizer dispensers more visible, try to select a color that contrasts with the wall color

According to Federal Law and Life Safety Code Requirements, new healthcare aisles, corridors and ramps used for exit access in a hospital or nursing home must be at least 8 feet clear and unobstructed.
When planning for construction, demolition, renovation or general maintenance, the healthcare facility undergoes a Preconstruction Risk Assessment for air quality, infection control, utility requirements, vibration, noise and other hazards that affect care, services and treatment. A tip is to designate someone to lead the Preconstruction Risk Assessment by making a plan to show and document information.

Fire extinguishers placed in kitchen grill areas should be Class K extinguishers. Class K extinguishers are specifically used for putting out grease-based fires. These extinguishers must be within 35 feet of all grease-producing appliances.

According to The Joint Commission, the answer is that facility team leaders do not know the location of their smoke compartments. It is advised that Facility Directors document where the facility's smoke compartments are and share this information with the rest of their team.

- Full U (Full Unannounced/Triennial)
- Med Def (Medicare Deficiency) - This survey type has a 50% rate of returned visits
- SSU/OQPS (Special Survey Unit & Office of Quality and Patient Safety)
- ICM 2 or 3 (Intracycle Monitoring)
- Extension Survey (New Building/Services)

No. It is not compliant to have a door between a hospital and non-hospital space for providers to go back and forth. The only time this is acceptable is in the case of a fire escape door. This fire escape door would have to be locked at all times. When the fire alarm is activated, the fire escape door would unlock electronically. A full floor to ceiling wall that meets all LSC requirements is the only acceptable option to separate space between a hospital and non-hospital.

A new table was added to assist designers and facility owners to determine which procedures should be performed in each room type. It should be noted that you should not add procedures or services in existing rooms based upon the chart without first checking with DAAC.
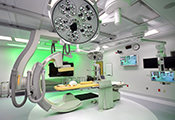
This would be enough power to make a steel fire extinguisher come off the wall. Any room within a hospital that contains an MRI machine should only be using non-ferrous or non-magnetic extinguishers.
- Fire response plan, LIP, copy at operator or security (EC.02.03.01 EP-9)
- Stairwell signage (floor information) tactile (LS.02.01.20 EP-10)
- Kitchen hood extinguishing (FA/Energy/Fans) (EC.02.03.05 EP-13)
- Succession plan and delegation of authority (EM.02.01.01 EP-12)
- Generator EPO remote/not on exterior enclosures (EC.02.05.03 EP-11)
- Corridor/Suite Perimeter Doors (LC.02.01.30 EP-13)

- Triennial 4 hours generator run applies to all HAP/AHC (EC.02.05.07 EP’s 9&10)
- Written surgical fire risk assessment and plan (EC.02.03.01 EP-11)
- Exit sign testing with batteries (EC.02.05.07 EP-1)
- Elevator fire fighter operations monthly test (EC.02.03.05 EP-27)
- LIM’s (EC.02.05.05 EP-7)
Here are some tips for success during your Facility Orientation:
- Make sure you know the location of the electrical panel with the designated breaker for the fire alarm.
- Know the number and types of sprinklers so you can determine the number of spares needed.
The Facility Orientation is the first step of the two day LSCS and should take about an hour.

- 59% Non-Compliant: Manage systems for extinguishing fires including the integrity (nothing supported by sprinkler piping, missing escutcheons)
- 41% Non-Compliant: Sprinkler heads are not damaged; They are free of corrosion, foreign materials, paint and have necessary escutcheon plates installed
- 34% Non-Compliant: Other issues, including blocked access to fire extinguishers (wildcard)

All columns along the perimeter of the wall, any furr-outs along the columns and exterior wall material are all included in exterior wall thickness. Want to learn more healthcare design tips?

According to Section 19.7.5.7.2 of the Life Safety Code, the answer is yes. Bins used for patient records waiting to be disposed of should meet FM Approval Standard 6921 requirements. Other waste bins used for reasons besides recycling clean waste and/or patient records waiting to be disposed of, do not have to meet FM Approval Standard 6921 requirements.

This 2018 edition of the Facility Guidelines Institute Guidelines includes three separate versions specifically for hospitals; outpatient facilities; and residential health, care and support facilities. Until October of 2018, the Department of Health is permitting the implementation of FGI Guidelines from the 2014 edition and 2018 edition for new projects. After that, only the 2018 edition will be valid.
No more Direct and Indirect EP designations
- Consolidate ESC into one 60-day time frame
- No more A or C categories
No more Opportunities for Improvement (OFI's)
- No more Measure of Success (MOS) See it/Cite it Survey Methodology
*Note: This does not apply to Sentinel Events where a MOS is required. At this time, the submittal of a MOS for Sentinel Events is still required.

Although, the requirement for access or direct visibility to the outside environment has been deleted since the LSC 2009 edition, the design of new hospital patient sleeping rooms should still be designed with visibility to the outside world. Many local building codes and state agencies overseeing hospital development require windows in patient sleeping rooms. Plus, there is a significant amount of evidence that human beings have a psychological need to see the outside and that aids in the healing process.
Bedroom: Each bedroom must accommodate no more than four residents each. Facilities that have been approved for construction or facilities certified after November 28, 2016 must accommodate no more than two residents per bedroom.
Bathroom: Each individual resident bedroom must be located near a toilet and bathing facilities or be equipped with such. Facilities that have been approved for construction or facilities certified after November 28, 2016 must equip each residential bedroom with a bathroom. The bathroom must include at least a sink and a toilet.

The label may be removed and doing so is identical to rendering the door as other than a fire protection rated door. Although you may remove the label, covering the label is not allowed. One last thing to note is that the provisions of NFPA 80 do not apply here.

Patients that are too weak to get out of bed are not required to be moved outside or to a safe area during a fire drill. Staff could simulate the relocation of bedridden patients using empty wheelchairs and replicated patients.
- When the facility is undergoing an addition or renovation, dust and contaminants from construction need to be managed.
- Hospital pharmacies need to make sure no contamination of sterile compounds takes place.
- Conscious patient areas need to have correct pressurization and ventilation.
- Utility and portable water systems need to be checked for Legionella growth.
- Addition
- Change of Use or Occupancy Classification
- Modification
- Reconstruction
- Renovation
- Repair

- Safe
- Effective
- Patient-Centered
- Timely
- Efficient
- Equitable
These six domains come from the Institute of Medicine's definition of quality care in a healthcare setting. Many other organizations use these domains as their general standard such as the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HSS).

Out of all the areas including stairs, enclosures, ramps, corridors and exit passageways, which one does not have strict guidelines for the exact location of handrails? The answer is corridors. Even though there is no guidelines on handrails for corridors, there are other codes to consider including complying with ADA requirements.

Yes. Since these offsite locations are usually considered business occupancies, the requirement is once per shift per year, but this also depends on who your facility is accredited by and the entity that is enforcing the Life Safety Code.

This all depends on who the authority is that has jurisdiction. If the storage equipment items qualify as construction, alterations, additions or repair, you may be able to store the items in the unused patient rooms. Of course, alternate life safety standards need to be followed and you should be following in accordance with your own policies as well.

When a play area or breast-feeding room is located near a specific department, they are to be included in the department’s DGSF. The exception is when play areas and breast-feeding rooms are positioned in a lobby or public space then they would be considered public spaces.

If the public can access your building, then you are most likely going to need emergency egress lighting. However, based on the Code, the most general rule is emergency egress lighting is needed when you are required to have two or more paths of egress and/or have delayed egress locking on doors.

This can also be done more frequently if needed.

- Ramps
- Stairs
- Doors
- Fire escape ladders
- Horizontal exits
- Smokeproof enclosures
- Exit passageways
- Areas of refuge
- Alternating thread devices
Notice that elevators are not on the list.

While Healthcare and Ambulatory Care may be acceptable classifications, an Emergency Department would never be considered a Business Occupancy. This is because not all patients brought to an Emergency Department are able to walk or speak, so that takes Business Occupancy off the table.
If Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approved a waiver or equivalency, you should be going through the process repeatedly every three years. This statement is still true even if things have not changed.

A risk assessment is beneficial when deciding if patients should be allowed to bring personal laptops, hairdryers and other electronic equipment into the hospital. Healthcare facilities are expected to develop a course of action to recognize patients' personal equipment that would be included in the medical equipment management plan.

Drawing submissions are required to go to DLS for I-2 and outpatient surgery centers. All hospital based departments, including business occupancies, must submit their narrative in correspondence to DAAC. All additions and alterations are going to be submitted to local code.

All fire-rated door decorating should be looked at as a no-go during festivities.